Logical NOT operator
Logical NOT is one of the unary operators in Javascript. A unary operator is an operator where no of operands is 1.
Syntax:
This is the syntax for the logical NOT operator
!operandor!expression
Execution steps for Logical NOT:
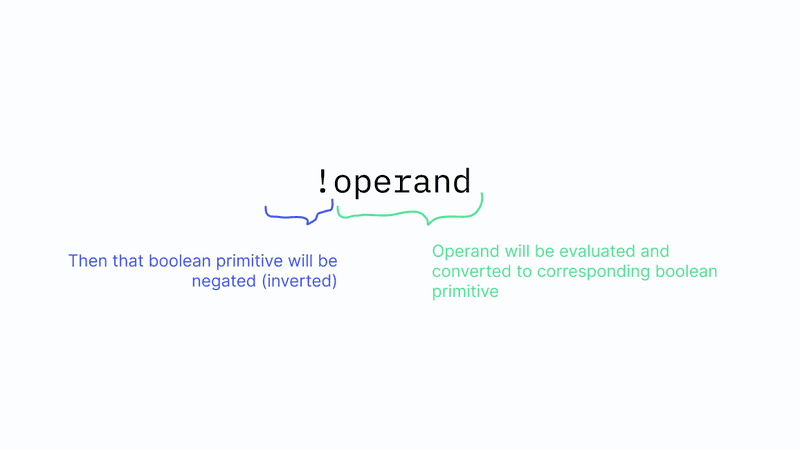
The execution of logical NOT expression happens in these steps.
- First, the operand or expression is evaluated
- Then evaluated value is coerced to the corresponding Boolean primitive.
- Now the result from step 2 will be logically negated.
Example:
!(2 + "1")// 1. !("21")// 2. !(true)// 3. false// so the result is `false`
Note: Conversion of any value to Boolean primitive:
Rules for coercion of any value to boolean primitive are straightforward
- If the value of type Boolean, return it.
- If the value is any of these values ( undefined, null, -0, +0, 0, “”, ‘’, ``, NaN ) or value is any object having the [[IsHTMLDDA]] internal slot such as the
document.all, then return false - In any other case, return true.
Examples of Logical NOT:
console.log(![]) // falseconsole.log(![""]) // falseconsole.log(![null]) // falseconsole.log(![undefined]) // falseconsole.log(![0]) // falseconsole.log(![NaN]) // falseconsole.log(!["abc"]) // falseconsole.log(![[]]) // falseconsole.log(![{}]) // falseconsole.log(!{}) // falseconsole.log(!{ a: "b" }) // falseconsole.log(!true) // falseconsole.log(!false) // trueconsole.log(!0) // trueconsole.log(!1) // falseconsole.log(!1.23) // falseconsole.log(!-1.23) // falseconsole.log(!-0.23) // falseconsole.log(!NaN) // trueconsole.log(!null) // trueconsole.log(!undefined) // trueconsole.log(!"") // trueconsole.log(!"abc") // falseconsole.log(!"123") // falseconsole.log(!"0") // falseconsole.log(!function abc() {}) // falseconsole.log(!new Function()) // false
Usage of logical NOT
- Calculate the corresponding boolean primitive of any value
Logical NOT can be used to calculate the corresponding boolean primitives of a non-boolean value
For e.g.:
const value = "abc"const equivalentBooleanValue = !!valueconsole.log(equivalentBooleanValue) // true
- If the value is of type Boolean then
!!value === value // in the case when the value is boolean.